Is there really seaweed in my ice cream?
Yep! Ice cream contains naturally-occurring, non-digestible carbohydrate ingredients, like guar, tara, and carrageenan gums. These ingredients bind up and distribute water during freezing, so that the frozen ice cream maintains a smooth (rather than a grainy or icy) texture.
These noted ingredients all have varied plant and microbial origins, but carrageenan gum itself is truly isolated from red seaweed!
These noted ingredients all have varied plant and microbial origins, but carrageenan gum itself is truly isolated from red seaweed!

Why does an apple turn brown after slicing it?
This browning effect is caused by an enzyme—Polyphenol oxidase or PPO—that is naturally present in the apple itself.
When an apple is sliced, tissue cells located along the cut surface become ruptured or broken. This cell rupture allows PPO enzymes and other cell constituents to combine and react to create the brown discoloration. Though the apple looks less appetizing—it is still safe to eat.
When an apple is sliced, tissue cells located along the cut surface become ruptured or broken. This cell rupture allows PPO enzymes and other cell constituents to combine and react to create the brown discoloration. Though the apple looks less appetizing—it is still safe to eat.

Why do Rice Krispies® go “snap, crackle, and pop” when milk is added?
Rice Krispies® consist of puffed, highly porous, dried pieces of rice. Each piece possesses many internal tunnels and connected air spaces.
As milk is added, it enters the many pores and tunnels within a puffed rice piece, concentrating and pressuring the air within these internal spaces to the point that the walls of these structures shatter—creating the “snap, crackle, pop” sounds.
As milk is added, it enters the many pores and tunnels within a puffed rice piece, concentrating and pressuring the air within these internal spaces to the point that the walls of these structures shatter—creating the “snap, crackle, pop” sounds.

What prevents ready-to-eat (RTE) cereal from getting soggy in milk?
RTE cereals are first dried to the very low levels of moisture (1-3%) needed to achieve crispness.
Individual cereal pieces are coated or sprayed with molten sugar, honey or other carbohydrate ingredients (starch, maltodextrin, dextrins, inulin, gums, etc.) to create a moisture barrier or thin film at the surface of pieces to slow the penetration of milk—extending the “bowl-life.”
Individual cereal pieces are coated or sprayed with molten sugar, honey or other carbohydrate ingredients (starch, maltodextrin, dextrins, inulin, gums, etc.) to create a moisture barrier or thin film at the surface of pieces to slow the penetration of milk—extending the “bowl-life.”
Why do M&M'S® not melt in your hand?
The chocolate center within the candies is coated with multiple layers of a corn syrup/sugar solution, with each individual layer allowed to dry or harden before a successive coat is applied.
This multi-layer, confectionery coating does not melt in the hand—but does dissolve in the mouth with the aid of moisture present in the saliva.
This multi-layer, confectionery coating does not melt in the hand—but does dissolve in the mouth with the aid of moisture present in the saliva.

What causes Wintergreen Life Savers® to spark when you bite them?
The sparking is an effect of triboluminescence, which occurs as sugar crystals within the candy are fractured by mechanical force (in this case chewing).
The structural change to sugar crystals results in the release of energy that is absorbed by nitrogen in the air and a flavor compound (methyl salicylate) in the mints, both of which emit visible light as they return to ground state.
The structural change to sugar crystals results in the release of energy that is absorbed by nitrogen in the air and a flavor compound (methyl salicylate) in the mints, both of which emit visible light as they return to ground state.

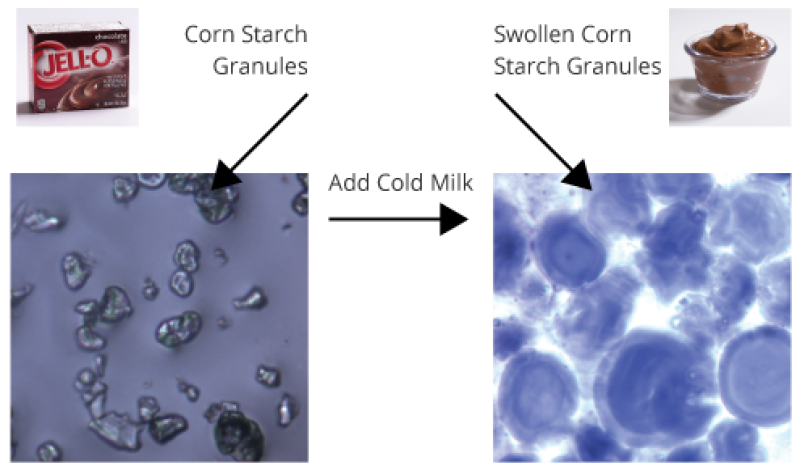
How does “instant” pudding thicken without heating?
Corn starch in “instant” pudding has been physically changed so that heating is no longer required for thickening.
When milk is added, corn starch granules rapidly absorb liquid and swell to many times their original size (see diagram). Imagine a room packed full of inflated balloons—think about how much friction you would encounter if you tried to walk through it! Corn starch thickens pudding in this way.
When milk is added, corn starch granules rapidly absorb liquid and swell to many times their original size (see diagram). Imagine a room packed full of inflated balloons—think about how much friction you would encounter if you tried to walk through it! Corn starch thickens pudding in this way.